Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 7:Adenoma"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Images == <gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> File:IPLab7Adenoma1.jpg|This is a low-power photomicrograph of a nodule found in the thyroid of this case. Note that the ...") |
(→Images) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Clinical Summary == | ||
| + | This 80-year-old white female's death came as the result of cardiopulmonary disease -- hypertension, coronary artery disease, pulmonary emphysema and cardiac hypertrophy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | During a routine postmortem examination, this patient's thyroid gland was found to be nodular. The right lobe contained several colloid nodules. Located in the left lobe was a 2-cm well-circumscribed mass. | ||
| + | |||
== Images == | == Images == | ||
<gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> | <gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> | ||
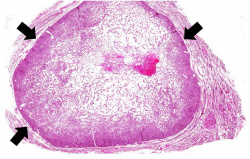
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab7Adenoma1b.jpg|This is a low-power photomicrograph of a nodule found in the thyroid of this case. Note that the mass is well-circumscribed and there is a sharp line of demarcation between the mass and the adjacent thyroid tissue (arrows). |
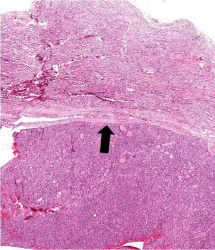
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab7Adenoma2b.jpg|This is a higher-power view of the border between the tumor mass and the adjacent thyroid tissue. Note that the mass has a capsule (arrow). Also note the different morphology between the adenoma on the bottom (very cellular, dense follicles) and the adjacent normal thyroid (larger follicles, colloid). |
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab7Adenoma3b.jpg|This is another higher-power photomicrograph of the adenoma (bottom) and the adjacent thyroid tissue (top). Note the capsule(*) separating the adenoma from the adjacent normal thyroid tissue. |
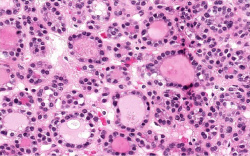
| − | + | File:IPLab7Adenoma4b.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of the adenoma. Note that the follicular architecture is well developed throughout this section. | |
| − | File: | ||
| − | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Virtual Microscopy == | ||
| + | <peir-vm>IPLab7Adenoma</peir-vm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Study Questions == | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is the likelihood that this tumor would have been 'hot' or would have taken up radioactive iodine?">Benign tumors are more likely to take up radioactive iodine than malignant tumors.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What are the differential diagnoses for thyroid masses?">Goiter, adenomas, neoplastic tumors of the thyroid.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="Although usually asymptomatic, what important clinical problems can occur in patients with benign thyroid adenomas?">They may: | ||
| + | # increase in size and cause pressure symptoms in the neck, | ||
| + | # achieve a certain size and then plateau, | ||
| + | # suddenly enlarge and become painful owing to intralesional hemorrhage, and | ||
| + | # rarely synthesize T3 or T4 and cause hyperthyroidism that is usually mild and unassociated with ophthalmopathy.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="Is someone with a thyroid adenoma at risk for thyroid carcinoma?">No. The risk of malignant transformation is almost negligible.</spoiler> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Additional Resources == | ||
| + | === Reference === | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/850823-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Evaluation of Solitary Thyroid Nodule] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/127491-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Thyroid Nodule] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Journal Articles === | ||
| + | * Tonacchera M, Vitti P, Agretti P, Ceccarini G, Perri A, Cavaliere R, Mazzi B, Naccarato AG, Viacava P, Miccoli P, Pinchera A, Chiovato L. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10566665 Functioning and nonfunctioning thyroid adenomas involve different molecular pathogenetic mechanisms]. ''J Clin Endocrinol Metab'' 1999 Nov;84(11):4155-8. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Images === | ||
| + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/140-thyroid PEIR Digital Library: Thyroid Images] | ||
| + | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/ENDOHTML/ENDOIDX.html WebPath: Endocrine Pathology] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Related IPLab Cases == | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 6:Graves Disease|Lab 6: Thyroid: Graves Disease]] | ||
{{IPLab 7}} | {{IPLab 7}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 7]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 7]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:52, 9 July 2020
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 80-year-old white female's death came as the result of cardiopulmonary disease -- hypertension, coronary artery disease, pulmonary emphysema and cardiac hypertrophy.
During a routine postmortem examination, this patient's thyroid gland was found to be nodular. The right lobe contained several colloid nodules. Located in the left lobe was a 2-cm well-circumscribed mass.
Images[edit]
This is a higher-power view of the border between the tumor mass and the adjacent thyroid tissue. Note that the mass has a capsule (arrow). Also note the different morphology between the adenoma on the bottom (very cellular, dense follicles) and the adjacent normal thyroid (larger follicles, colloid).
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Evaluation of Solitary Thyroid Nodule
- eMedicine Medical Library: Thyroid Nodule
Journal Articles[edit]
- Tonacchera M, Vitti P, Agretti P, Ceccarini G, Perri A, Cavaliere R, Mazzi B, Naccarato AG, Viacava P, Miccoli P, Pinchera A, Chiovato L. Functioning and nonfunctioning thyroid adenomas involve different molecular pathogenetic mechanisms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999 Nov;84(11):4155-8.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
Pulmonary emphysema is a condition in which the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles are permanently increased in size due to either destruction of the wall or alveolar dilatation.
Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate--characterized by large discrete prostatic nodules--is a common disorder in men over 50 years of age. The nodules cause the prostate to be enlarged and to have an increased weight. The human prostate is surrounded by a restrictive capsule. These nodules cause increased pressure within the capsule which leads to constriction of the urethra as it passes through the prostate. Urethral constriction leads to retention of urine.