Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 7:Metastatic Adenocarcinoma"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
(→Clinical Summary) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Clinical Summary == | == Clinical Summary == | ||
| − | This 58-year-old male was admitted five weeks earlier with a weight loss of 80 pounds over a six-month period, abdominal cramps, and rebound tenderness in the right lower quadrant. Abdominal and chest | + | This 58-year-old male was admitted five weeks earlier with a weight loss of 80 pounds over a six-month period, abdominal cramps, and rebound tenderness in the right lower quadrant. Abdominal and chest imaging showed multiple nodular masses in the lungs and liver. Fine needle biopsy of the liver revealed adenocarcinoma with the primary source thought to be colon. He was discharged on chemotherapy, but returned two days later with small bowel obstruction and sepsis, and he died a few days later. |
| + | |||
| + | Autopsy revealed an obstructive firm mass in the cecum with similar masses in the lungs, lymph nodes, liver and peritoneum. A large retrocecal abscess was found. Blood cultures grew Klebsiella pneumoniae and E. coli. | ||
== Autopsy Findings == | == Autopsy Findings == | ||
Revision as of 01:49, 9 July 2020
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
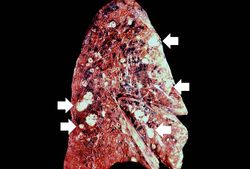
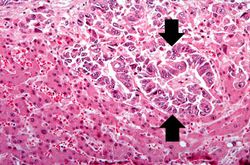
This 58-year-old male was admitted five weeks earlier with a weight loss of 80 pounds over a six-month period, abdominal cramps, and rebound tenderness in the right lower quadrant. Abdominal and chest imaging showed multiple nodular masses in the lungs and liver. Fine needle biopsy of the liver revealed adenocarcinoma with the primary source thought to be colon. He was discharged on chemotherapy, but returned two days later with small bowel obstruction and sepsis, and he died a few days later.
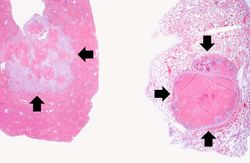
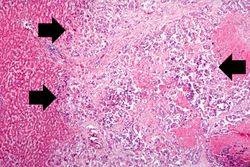
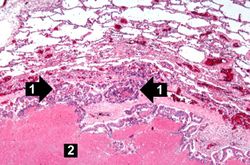
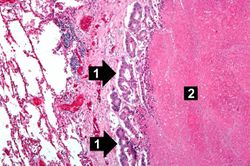
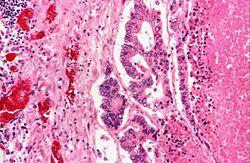
Autopsy revealed an obstructive firm mass in the cecum with similar masses in the lungs, lymph nodes, liver and peritoneum. A large retrocecal abscess was found. Blood cultures grew Klebsiella pneumoniae and E. coli.
Autopsy Findings[edit]
Autopsy revealed an obstructive firm mass in the cecum with similar masses in the lungs, lymph nodes, liver and peritoneum. A large retrocecal abscess was found. Blood cultures grew Klebsiella pneumoniae and E. coli.
Images[edit]
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Lung[edit]
Liver[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Imaging in Adenocarcinoma of the Colon
- eMedicine Medical Library: Colon Adenocarcinoma
- Merck Manual: Colorectal Cancer
- Merck Manual: Metastatic Liver Cancer
Journal Articles[edit]
- Castro CY, Moran CA, Flieder DG, Suster S. Primary signet ring cell adenocarcinomas of the lung: a clinicopathological study of 15 cases. Histopathology 2001 Oct;39(4):397-401.
Images[edit]
- PEIR Digital Library: Adenocarcinoma Images
- PEIR Digital Library: Metastatic Adenocarcinoma Images
- WebPath: Hepatic Neoplasms
- WebPath: Lung Neoplasms
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
- Lab 7: Colon: Adenocarcinoma
- Lab 7: Lip: Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Lab 7: Esophagus: Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Lab 7: Breast: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma
- Lab 7: Lung: Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate--characterized by large discrete prostatic nodules--is a common disorder in men over 50 years of age. The nodules cause the prostate to be enlarged and to have an increased weight. The human prostate is surrounded by a restrictive capsule. These nodules cause increased pressure within the capsule which leads to constriction of the urethra as it passes through the prostate. Urethral constriction leads to retention of urine.
An abscess is a collection of pus (white blood cells) within a cavity formed by disintegrated tissue.