Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 6:Tuberculosis"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
(→Autopsy Findings) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == Clinical Summary == | + | == Clinical Summary == |
| − | + | During the course of a routine physical examination two months prior to admission, this 57-year-old white male was noted to have a lesion in the upper lobe of the right lung. Initially, he was treated for two weeks with ampicillin. He was then admitted to an outside hospital for further study. All studies including sputum studies for tubercle bacilli, bronchial washings, and bronchoscopy were negative and he was discharged. Review of systems revealed the presence of mild dyspnea on exertion, accompanied by a slightly productive cough. Of interest was the fact that the patient had been PPD positive for the past 4 to 5 years, but this had never been evaluated. On this hospital admission, physical and laboratory examinations were negative. Radiographic examination of the chest revealed a 2 x 2-cm density in the right lower lung field. Several small cavities were identified in this area on CT scan. | |
| − | + | The patient underwent a thoracotomy, at which time a portion of the upper lobe of the right lung was removed. Examination of the cut surface revealed small white nodules measuring up to 0.2 cm in diameter. | |
| − | |||
== Images == | == Images == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
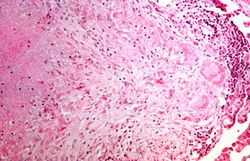
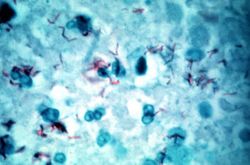
File:IPLab6TB6.jpg|This is a high-power (oil immersion) photomicrograph of granuloma stained with an acid-fast stain. Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacilli stain red. | File:IPLab6TB6.jpg|This is a high-power (oil immersion) photomicrograph of granuloma stained with an acid-fast stain. Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacilli stain red. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Virtual Microscopy == | ||
| + | === Lung: TB H&E === | ||
| + | <peir-vm>IPLab6TB_HE</peir-vm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Lung: TB AFGT === | ||
| + | <peir-vm>IPLab6TB_AFGT</peir-vm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Normal Lung === | ||
| + | <peir-vm>UAB-Histology-00107</peir-vm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Study Questions == | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is the Ghon complex?">In primary pulmonary TB you get (1) parenchymal subpleural lesions, often just above or just below the interlobar fissure, and (2) enlarged caseous lymph nodes draining the parenchymal focus (usually the hilar lymph nodes).</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What factors are responsible for the virulence of M. tuberculosis?">M. tuberculosis has no known exotoxins, endotoxins or histolytic factors. Its pathogenicity is due to the fact that it resists phagocytic killing and sets up a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. Virulent M. tuberculosis organisms have cord factor, sulfatides, LAM, heat shock protein and they activate complement.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is the sequence of events after primary exposure to M. tuberculosis?">The initial infection with M. tuberculosis leads to a T cell-mediated immune response that controls 95% of infections. Alveolar macrophages phagocytose the organisms and then transport them to the hilar lymph nodes. Macrophages cannot kill the mycobacteria so the organisms multiply, lyse the host cell, infect other macrophages, and sometimes disseminate via the blood to other parts of the lung and elsewhere in the body. | ||
| + | |||
| + | After a few weeks, T cell-mediated immunity develops and leads to activation of macrophages so they can kill intracellular mycobacteria via reactive nitrogen intermediates. This process leads to formation of epithelioid cell granulomas and clearance of the mycobacteria. Also, CD8+ suppresser T cells kill macrophages that are infected with mycobacteria, resulting in the formation of caseating granulomas. These processes during the primary infection with M. tuberculosis result in a calcified scar in the lung parenchyma and in the hilar lymph node. This combination is called the Ghon complex. | ||
| + | </spoiler> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Additional Resources == | ||
| + | === Reference === | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/230802-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Tuberculosis] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/infectious_diseases/mycobacteria/tuberculosis_tb.html Merck Manual: Tuberculosis (TB)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Journal Articles === | ||
| + | * Rodrigues DS, Medeiros EA, Weckx LY, Bonnez W, Salomão R, Kallas EG. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11982602 Immunophenotypic characterization of peripheral T lymphocytes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and disease]. ''Clin Exp Immunol'' 2002 Apr;128(1):149-54. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Images === | ||
| + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/259-tuberculosis PEIR Digital Library: Tuberculosis Images] | ||
| + | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/LUNGHTML/LUNGIDX.html#4 WebPath: Granulomatous Diseases] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Related IPLab Cases == | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 1:Tuberculosis|Lab 1: Lung: Tuberculosis (Caseous Necrosis)]] | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 3:Tuberculosis|Lab 3: Lung: Tuberculosis]] | ||
{{IPLab 6}} | {{IPLab 6}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 6]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 6]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:39, 8 July 2020
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
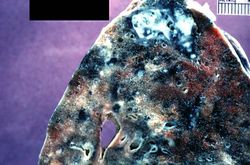
During the course of a routine physical examination two months prior to admission, this 57-year-old white male was noted to have a lesion in the upper lobe of the right lung. Initially, he was treated for two weeks with ampicillin. He was then admitted to an outside hospital for further study. All studies including sputum studies for tubercle bacilli, bronchial washings, and bronchoscopy were negative and he was discharged. Review of systems revealed the presence of mild dyspnea on exertion, accompanied by a slightly productive cough. Of interest was the fact that the patient had been PPD positive for the past 4 to 5 years, but this had never been evaluated. On this hospital admission, physical and laboratory examinations were negative. Radiographic examination of the chest revealed a 2 x 2-cm density in the right lower lung field. Several small cavities were identified in this area on CT scan.
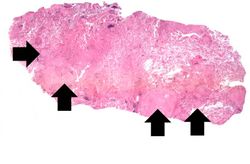
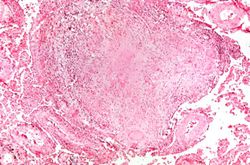
The patient underwent a thoracotomy, at which time a portion of the upper lobe of the right lung was removed. Examination of the cut surface revealed small white nodules measuring up to 0.2 cm in diameter.
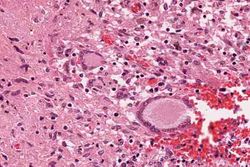
Images[edit]
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Lung: TB H&E[edit]
Lung: TB AFGT[edit]
Normal Lung[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
Journal Articles[edit]
- Rodrigues DS, Medeiros EA, Weckx LY, Bonnez W, Salomão R, Kallas EG. Immunophenotypic characterization of peripheral T lymphocytes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and disease. Clin Exp Immunol 2002 Apr;128(1):149-54.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
Mycobateria grow very slowly on culture plates, with cultures requiring up to 6 weeks for a positive finding. In lieu of cultures, a more rapid diagnostic test is the PPD--purified protein derivative of tuberculosis--test. PPD is injected under the skin of an individual and then the area is reexamined in 48-72 hours for signs of an inflammatory reaction. A positive test indicates previous exposure to M. tuberculosis.
A thoracotomy is a surgical procedure in which an opening is made in the chest wall.
Caseous means cheesy.
A normal PaCO2 is 35 to 45 mmHg.