Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 6:Rheumatoid Arthritis"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
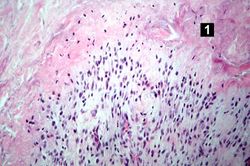
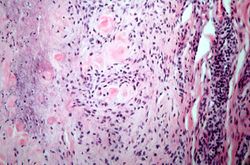
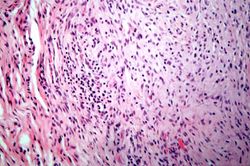
File:IPLab6RA10.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of another region with macrophages (right), fibrocytes (left), and occasional lymphocytes throughout the lesion. | File:IPLab6RA10.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of another region with macrophages (right), fibrocytes (left), and occasional lymphocytes throughout the lesion. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Study Questions == | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is pannus?">Inflamed and hyperemic synovium.</spoiler> | ||
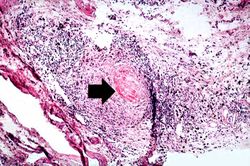
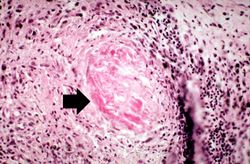
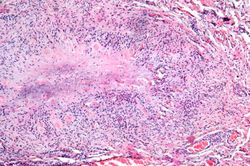
| + | * <spoiler text="How common are rheumatoid nodules and what are they?">Rheumatoid nodules occur in 25% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Rheumatoid nodules occur on pressure points (elbows, occiput, lumbosacral area, foot) and are composed of a central area of fibrinoid necrosis surrounded by a rim of epithelioid macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. The morphology of the rheumatoid nodule is similar to the tissue reaction seen in the joints.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="The exact pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is not known. What are some of the factors that are associated with RA?">Genetic susceptibility, exposure to a primary exogenous arthritogen, an autoimmune reaction within the synovial membranes, and release of cytokines that mediate joint damage.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is rheumatoid factor?">IgM antibodies (perhaps originating from the joints) that are directed against the Fc portion of autologous IgG.</spoiler> | ||
{{IPLab 6}} | {{IPLab 6}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 6]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 6]] | ||
Revision as of 15:17, 21 August 2013
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 57-year-old white female had suffered from rheumatoid arthritis for 20 years. During this period, many joints were involved, some seriously. Because of the severe pain of this arthritis the patient was placed on steroids and was given analgesics, some of which contained acetaminophen. The patient also took additional analgesics (aspirin and/or acetaminophen) to help control the pain. The patient was admitted to the emergency room for weakness and hematemesis. On admission the patient's hematocrit was 21%. Endoscopy demonstrated a large bleeding ulcer and fresh blood in the stomach and proximal duodenum. The sites of bleeding were cauterized; however, shortly after the procedure the patient became hypotensive and died despite aggressive resuscitation.
Autopsy Findings[edit]
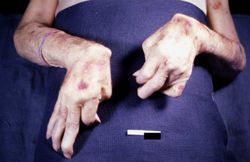
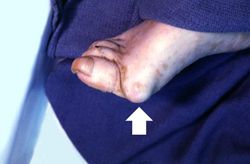
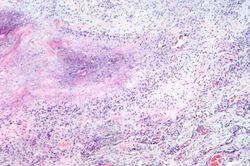
There were numerous erosions and ulcers in the gastrointestinal tract and a large quantity of fresh blood in the gastrointestinal tract. There was also significant swelling and deformation in multiple joints. On the medial aspect of the right foot there was a firm, irregular, rubbery subcutaneous nodule measuring 2 x 1.5 cm. The cut surface was whitish-yellow and fibrous.
Images[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood.
A hematocrit value represents the number of packed red cells in mL per 100 mL of centrifuged whole blood--expressed as a percentage. A normal hematocrit for a female is 34 to 44%.
Autoimmune disorders involve an immune response directed at the host's own cells.