Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 6:Chronic Rejection"
(→Surgical Pathology Findings) |
(→Images) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Images == | == Images == | ||
<gallery height="250px" widths="250px"> | <gallery height="250px" widths="250px"> | ||
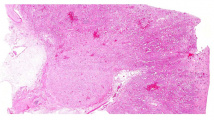
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection1b.jpg|This is a low-power photomicrograph of the kidney from this case of chronic transplant rejection. Note the focal areas of hemorrhage and inflammatory cell infiltrate in this section. |
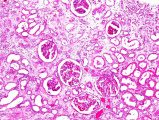
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection2b.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of kidney with congestion and sclerosis of the glomeruli. Note that there is a marked loss of renal tubules throughout this section with replacement by fibrous connective tissue. Also note the cellularity of the glomeruli. |
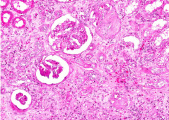
| − | + | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection3b.jpg|This is another area of renal cortex similar to the previous image. Note the fibrosis and loss of renal tubules throughout this section. | |
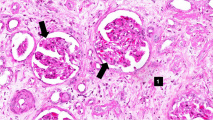
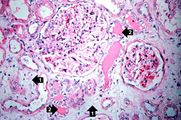
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection4b.jpg|This high-power photomicrograph of glomeruli from this kidney demonstrating increased cellularity with mesangial expansion (arrows). There is generalized loss of tubules and replacement by fibrosis in this section (1) |
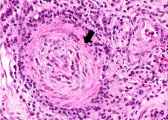
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection5b.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of rejected kidney with cellular infiltrates and a small artery with neointimal proliferation and stenosis (arrow). |
| − | File: | ||
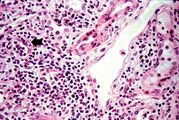
File:IPLab6ChronicRejection7.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of a glomerulus with a mild cellular infiltrate (left) and a small damaged glomerulus (right). There is extensive interstitial fibrosis (1), loss of renal tubules, and the remaining tubules contain protein (2) indicating severe damage. | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection7.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of a glomerulus with a mild cellular infiltrate (left) and a small damaged glomerulus (right). There is extensive interstitial fibrosis (1), loss of renal tubules, and the remaining tubules contain protein (2) indicating severe damage. | ||
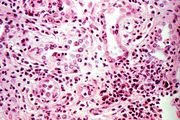
File:IPLab6ChronicRejection8.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of renal cortex with cellular infiltrate and few remaining renal tubules. The cellular infiltrate comprises macrophages, activated (large) lymphocytes and a few neutrophils and plasma cells. | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection8.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of renal cortex with cellular infiltrate and few remaining renal tubules. The cellular infiltrate comprises macrophages, activated (large) lymphocytes and a few neutrophils and plasma cells. | ||
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection9b.jpg|This high-power photomicrograph demonstrates the characteristic manifestations of chronic antibody-mediated rejection. The glomerulus shows inflammatory cells within the capillary loops (glomeruliitis), accumulation of mesangial matrix, and duplication (or multilamination) of the capillary basement membrane (arrow). |
File:IPLab6ChronicRejection10.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of a kidney from another case of chronic transplant rejection. In this case there is extensive damage to the kidney due to the chronic rejection (loss of tubules and glomerular lesions). In addition, this kidney was removed during an episode of acute rejection. The marked cellular infiltrate indicates acute rejection in a case of chronic transplant rejection. | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection10.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of a kidney from another case of chronic transplant rejection. In this case there is extensive damage to the kidney due to the chronic rejection (loss of tubules and glomerular lesions). In addition, this kidney was removed during an episode of acute rejection. The marked cellular infiltrate indicates acute rejection in a case of chronic transplant rejection. | ||
File:IPLab6ChronicRejection11.jpg|This is a higher-power photomicrograph of kidney from the previous image demonstrating the cellular infiltrate which is comprised of lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells and a few neutrophils. | File:IPLab6ChronicRejection11.jpg|This is a higher-power photomicrograph of kidney from the previous image demonstrating the cellular infiltrate which is comprised of lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells and a few neutrophils. | ||
Latest revision as of 00:08, 9 July 2020
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 39-year-old male had malignant hypertension with malignant nephrosclerosis, progressing to chronic renal failure. He underwent a bilateral nephrectomy for control of his hypertension and received a cadaveric renal transplant. He did well, although his bllod pressure was elevated and his BUN and creatinine were gradually rising despite aggressive treatment. A transplant nephrectomy was performed 4 years after his transplant and he resumed hemodialysis.
The kidney weighed 125 grams and was covered by a thick capsule, which was partially adherent to the cortex, but could be stripped from the kidney with slight difficulty. The cortex was thinned but calyces and pelvis of the kidney appeared normal. The vessels were not prominent. The renal arteries and vein appeared normal.
Images[edit]
This high-power photomicrograph demonstrates the characteristic manifestations of chronic antibody-mediated rejection. The glomerulus shows inflammatory cells within the capillary loops (glomeruliitis), accumulation of mesangial matrix, and duplication (or multilamination) of the capillary basement membrane (arrow).
This is a high-power photomicrograph of a kidney from another case of chronic transplant rejection. In this case there is extensive damage to the kidney due to the chronic rejection (loss of tubules and glomerular lesions). In addition, this kidney was removed during an episode of acute rejection. The marked cellular infiltrate indicates acute rejection in a case of chronic transplant rejection.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Assessment and Management of the Renal Transplant Patient
- eMedicine Medical Library: Renal Transplantation
- eMedicine Medical Library: Malignant Hypertension
- Merck Manual: Hypertensive Emergencies
- Merck Manual: Chronic Kidney Disease
- Merck Manual: Hemodialysis
- Merck Manual: Kidney Transplantation
Journal Articles[edit]
- Matas AJ. Impact of acute rejection on development of chronic rejection in pediatric renal transplant recipients. Pediatr Transplant 2000 May;4(2):92-9.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
- Lab 1: Kidney: Infarction (Coagulative Necrosis)
- Lab 6: Kidney: Acute Transplant Rejection
- Lab 10: Kidney: Candidiasis
Hypertension which has caused end-organ damage is termed malignant. Without proper treatment, these patients will usually die in less than 2 years. Blood pressures in patients with malignant hypertension are frequently 160/110 mm Hg or greater.
Renal failure is the severe reduction of renal function and often leads to reduced urinary output.
These tests are measures of kidney function. High levels mean low function.
A normal gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) is 0 to 65 U/L.
An infiltrate is an accumulation of cells in the lung parenchyma--this is a sign of pneumonia.
An infiltrate is an accumulation of cells in the lung parenchyma--this is a sign of pneumonia.