Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 12:COPD"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Clinical Summary == | == Clinical Summary == | ||
| − | This 64-year-old man was hospitalized because of increasing shortness of breath, cough, increasing sputum production, and fever. The patient had a 75 pack-year history of cigarette smoking. On admission his respiratory rate was 20 breaths per minute and his pulse was 110 bpm. On room air his PaO2 was 46 mm Hg, his PaCO2 was 62 mm Hg, and the pH was 7.26. He was started on 24% O2 and after 6 hours his PaO2 was 52 mm Hg, his PaCO2 was 54 and his pH was 7.30. His hemoglobin was 17.1 g/dL, his PCV was 54%, and his leukocyte count was 15,300 cells/ | + | This 64-year-old man was hospitalized because of increasing shortness of breath, cough, increasing sputum production, and fever. The patient had a 75 pack-year history of cigarette smoking. On admission his respiratory rate was 20 breaths per minute and his pulse was 110 bpm. On room air his PaO2 was 46 mm Hg, his PaCO2 was 62 mm Hg, and the pH was 7.26. He was started on 24% O2 and after 6 hours his PaO2 was 52 mm Hg, his PaCO2 was 54 and his pH was 7.30. His hemoglobin was 17.1 g/dL, his PCV was 54%, and his leukocyte count was 15,300 cells/mm³ with 13% bands, 65% PMNs, 15% lymphocytes, 4% monocytes and 3% eosinophils. Chest x-ray showed a narrow heart silhouette, a low, flattened diaphragm, and markedly lucent regions in the upper lung fields suggesting areas of emphysema. An electrocardiogram showed tall P waves and a right axis deviation. The patient was given broad-spectrum antibiotics and was continued on his oral and inhalant bronchodilators and was started on a diuretic. His condition improved but two days after admission he suffered acute respiratory failure and could not be resuscitated. |
== Autopsy Findings == | == Autopsy Findings == | ||
Revision as of 00:52, 26 August 2013
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 64-year-old man was hospitalized because of increasing shortness of breath, cough, increasing sputum production, and fever. The patient had a 75 pack-year history of cigarette smoking. On admission his respiratory rate was 20 breaths per minute and his pulse was 110 bpm. On room air his PaO2 was 46 mm Hg, his PaCO2 was 62 mm Hg, and the pH was 7.26. He was started on 24% O2 and after 6 hours his PaO2 was 52 mm Hg, his PaCO2 was 54 and his pH was 7.30. His hemoglobin was 17.1 g/dL, his PCV was 54%, and his leukocyte count was 15,300 cells/mm³ with 13% bands, 65% PMNs, 15% lymphocytes, 4% monocytes and 3% eosinophils. Chest x-ray showed a narrow heart silhouette, a low, flattened diaphragm, and markedly lucent regions in the upper lung fields suggesting areas of emphysema. An electrocardiogram showed tall P waves and a right axis deviation. The patient was given broad-spectrum antibiotics and was continued on his oral and inhalant bronchodilators and was started on a diuretic. His condition improved but two days after admission he suffered acute respiratory failure and could not be resuscitated.
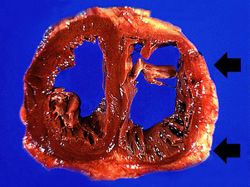
Autopsy Findings[edit]
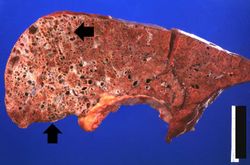
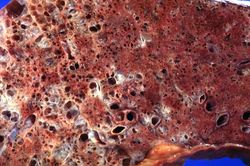
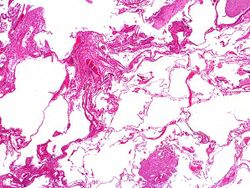
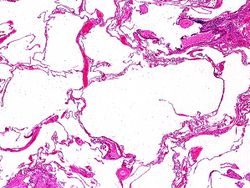
Pertinent autopsy findings included emphysema with moderate mucous plugging of bronchi. Right ventricular hypertrophy and dilation were also noted.
Images[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
Journal Articles[edit]
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
| |||||
Shortness of breath is a common clinical manifestation of heart failure.
A pack-year denotes smoking one pack of cigarettes per day for one year.
A normal respiratory rate is 10 to 20 breaths per minute.
A normal pulse rate is 60 to 100 bpm.
A normal PaO2 is 80 to 105 mm Hg.
A normal PaCO2 is 35 to 45 mmHg.
A normal arterial pH is 7.35 to 7.45.
A normal PaO2 is 80 to 105 mm Hg.
A normal PaCO2 is 35 to 45 mmHg.
A normal arterial pH is 7.35 to 7.45.
Normal hemoglobin for a male is 14 to 17.2 gm/dL.
A normal hematocrit for a male is 39 to 49%.
A normal white blood cell count is 4000-11,000 cells/mm³.
Band neutrophils are immature neutrophils in the circulation that indicates an increased demand, i.e. inflammation. Normal band levels in circulation are 3 to 5%.
Pulmonary emphysema is a condition in which the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles are permanently increased in size due to either destruction of the wall or alveolar dilatation.
Consolidation is the filling of lung air spaces with exudate--this is a sign of pneumonia.
In alcoholics, aspiration pneumonia is common--bacteria enter the lung via aspiration of gastric contents.