IPLab:Lab 1:Lung Abscess
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
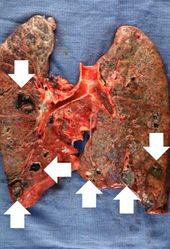
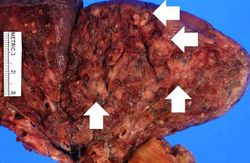
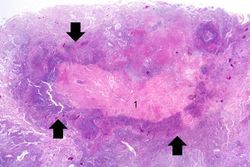
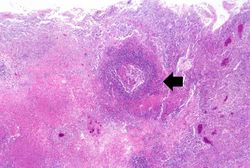
This 67-year-old male with advanced colon cancer underwent palliative surgery to remove a bowel obstruction. During the surgery the patient had several episodes of hypotension and after surgery he required ventilator support. Four days later the patient developed a fever and his white blood cell count was 15,256 cells/mm3. A chest x-ray demonstrated infiltrates in both lungs, which worsened over the next several days. His overall condition continued to deteriorate and he died 12 days after surgery. At autopsy, the lungs were markedly consolidated and had several focal abscesses that were 2 to 4 cm in diameter. Liquefied material poured out from these abscesses when the lungs were sliced.
Autopsy Findings[edit]
At autopsy, metastatic colon cancer was found throughout the abdominal cavity and invading into the liver. The lungs were markedly consolidated and had several focal abscesses that were 2 to 4 cm in diameter. Liquefied material poured out from inside these abscesses when the lungs were sliced.
Images[edit]
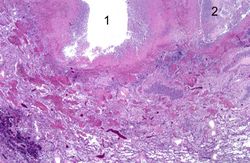
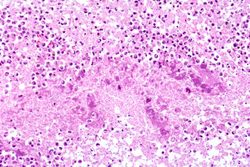
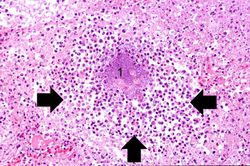
This higher-power photomicrograph of lung demonstrates the edge of the abscess. Note the loss of material from the center of the abscess (1) and loose necrotic material that has not been expelled (2). This material is made up of inflammatory cells (primarily dead white blood cells) and necrotic lung tissue.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Lung Abscess[edit]
Normal Lung[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
Journal Articles[edit]
- Brandenburg JA et al. Clinical presentation, processes and outcomes of care for patients with Pneumococcal pneumonia. J Gen Intern Med 2000 September; 15(9): 638–646.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
| |||||
Palliative surgery provides alleviation but is not curative.
An infiltrate is an accumulation of cells in the lung parenchyma--this is a sign of pneumonia.
Consolidation is the filling of lung air spaces with exudate--this is a sign of pneumonia.
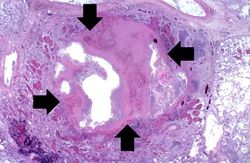
An abscess is a collection of pus (white blood cells) within a cavity formed by disintegrated tissue.
An abscess is a collection of pus (white blood cells) within a cavity formed by disintegrated tissue.
In alcoholics, aspiration pneumonia is common--bacteria enter the lung via aspiration of gastric contents.