Clinical Summary[edit]
This 56-year-old white female was admitted to the hospital with a six-year history of epigastric pain and burning. This pain was said to be worse at night and on an empty stomach. The patient reported that the pain was relieved by drinking milk. She had also experienced several episodes of hematemesis and melena since the onset of the pain, the last episode occurring 3 weeks prior to admission. The patient described intermittent episodes of colicky pain in the right upper quadrant and right side of the abdomen, frequently radiating to the back and shoulders and often accompanied by "bilious vomiting." Physical examination was noncontributory except for tenderness in the epigastrium and right upper quadrant. An upper GI series showed changes suggestive of a neoplasm. The patient submitted to an abdominal exploration at which time a partial gastrectomy was performed.
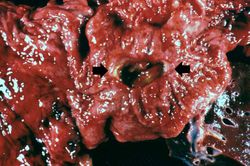
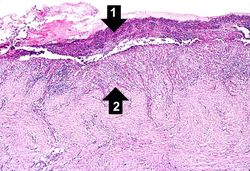
This is a gross photograph of a stomach containing an ulcer. Note the folded pink gastric mucosa that extends up to the edge of the ulcer (arrows).
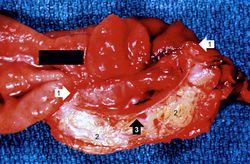
This is a gross photograph of the ulcer after it has been transected. The edge of the mucosa (1) is better appreciated in this image. Note the thick, fatty tissue (2) which makes up the base of this ulcer (3).
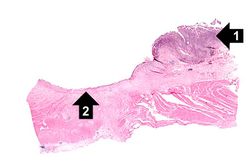
This is a low-power photomicrograph of the transected ulcer. The blue cells on the right hand side of this section are the normal gastric epithelial cells of the mucosa (1). Note the absence of any epithelial cells within the crater of the ulcer (2).
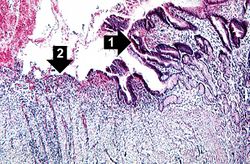
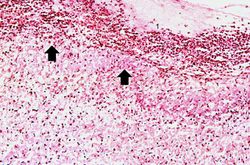
This is a photomicrograph of the margin of the ulcer. Note the intact epithelium on the right side of the section (1) and the ulcerated region without epithelium on the left (2). There are numerous inflammatory cells within this tissue.
This is a medium-power photomicrograph of the base of the ulcer with the fibrinopurulent membrane (1) overlying the ulcerated surface. The ulcerated surface contains granulation tissue and inflammatory cells (2).
This high-power photomicrograph of the ulcer base (arrows) demonstrates the lack of epithelium and the exuberant inflammatory response (1) consisting of primarily of fibrin (and adherent gastric secretions) and PMNs. The surface of the ulcer bed is covered with this fibrinopurulent exudate.
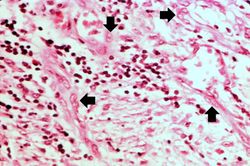
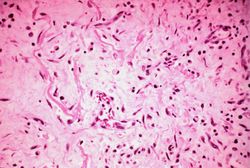
This high-power photomicrograph of the ulcer base demonstrates plump, activated fibroblasts and endothelial cells (arrows) within the granulation tissue that makes up the base of the ulcer. There are inflammatory cells (primarily lymphocytes) within this region as well.
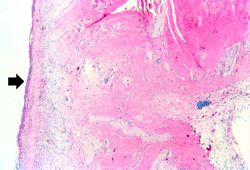
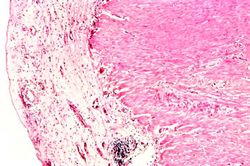
This low-power photomicrograph demonstrates the healing reaction in the base of this ulcer. The base of the ulcer is at the left-hand side of the image and the serosal surface is at the right. Note the fibrous connective tissue within the wall of the stomach and the layer of inflammatory exudate on the surface of the ulcer (arrow).
This high-power photomicrograph demonstrates the granulation tissue within the base of the ulcer.
This is a photomicrograph of the serosal surface (1) from a section of stomach near the ulcer. Note that the inflammatory reaction extends out to the serosa.
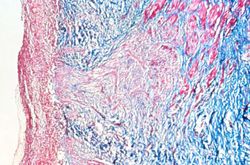
This is a trichrome-stained section of tissue demonstrating fibrous connective tissue scar formation (blue color) in this lesion. The surface of the ulcer is at the left-hand side of the image. There is a layer of inflammatory cells and RBCs on the surface of the ulcer.
Study Questions[edit]
Alcoholic cirrhosis, chronic obstructive airway disease, chronic renal disease, and hyperparathyroidism or any condition which leads to hypercalcemia (calcium stimulates gastrin production).
H. pylori is found in 90-100% of cases. It is thought that the H. pylori produce urease, leading to ammonia production and that they also produce a protease that breaks down glycoproteins in the mucus which forms the protective coat on the gastric mucosa.
The base of this chronic ulcer has a granulomatous inflammatory reaction composed of lymphocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. This is in contrast to the acute inflammatory reaction at the surface of the ulcer due to irritation from the acid and gastric contents.
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
Journal Articles[edit]