Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 4:Pulmonary Congestion and Edema"
(→Virtual Microscopy) |
(→Clinical Summary) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Clinical Summary == | == Clinical Summary == | ||
| + | This 67-year-old male was hospitalized because of extensive atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Following surgery, during which diseased portions of the femoral arteries were bypassed, he developed massive pulmonary embolization and expired. | ||
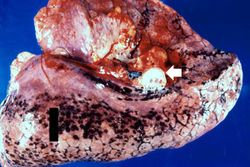
| − | + | At autopsy, thrombi were found in the femoral and iliac veins, as well as in the larger pulmonary arteries. | |
== Autopsy Findings == | == Autopsy Findings == | ||
Revision as of 01:53, 24 June 2020
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 67-year-old male was hospitalized because of extensive atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Following surgery, during which diseased portions of the femoral arteries were bypassed, he developed massive pulmonary embolization and expired.
At autopsy, thrombi were found in the femoral and iliac veins, as well as in the larger pulmonary arteries.
Autopsy Findings[edit]
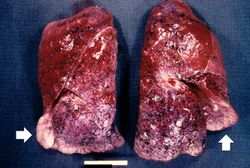
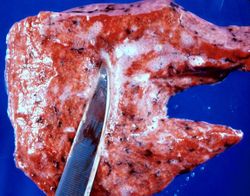
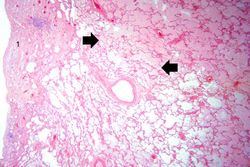
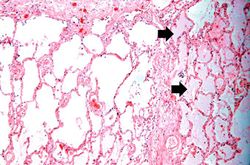
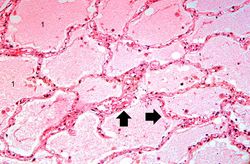
Significant findings at postmortem examination were old and recent myocardial infarctions and evidence of congestive heart failure. The right and left lungs weighed 950 grams and 750 grams, respectively, and were reddish-brown.
Images[edit]
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Lung: Congestion and Edema[edit]
Normal Lung[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
- Define the following:
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
Journal Articles[edit]
- Welch TD, Yang EH, Reeder GS, Gersh BJ. Modern management of acute myocardial infarction. Curr Probl Cardiol 2012 Jul;37(7):237-310.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
- Lab 1: Heart: Myocardial Infarction (Coagulative Necrosis)
- Lab 3: Heart: Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Lab 3: Heart: Healed Myocardial Infarction
- Lab 4: Heart: Mural Thrombus
- Lab 4: Coronary Artery: Thrombosis
| |||||
A normal right lung weighs 450 grams (range: 360 to 570 grams.
A normal left lung weighs 375 grams (range: 325 to 480 grams).
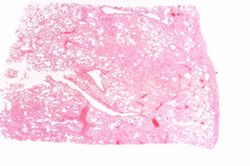
Pulmonary congestion is the engorgement of pulmonary vessels with blood. The increased pressure caused by this engorgement leads to transudation of fluid through the capillary walls and into the alveolar and interstitial spaces.