|
|
| Line 44: |
Line 44: |
| | | | |
| | === Images === | | === Images === |
| − | * [http://peir.path.uab.edu/library/index.php?/tags/115-hepatitis PEIR Digital Library: Hepatitis Images] | + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/115-hepatitis PEIR Digital Library: Hepatitis Images] |
| | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/LIVEHTML/LIVERIDX.html#5 WebPath: Viral Hepatitis] | | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/LIVEHTML/LIVERIDX.html#5 WebPath: Viral Hepatitis] |
| | | | |
Revision as of 01:42, 30 August 2013
Clinical Summary[edit]
This was a 55-year-old white male with chronic renal failure who acquired hepatitis B virus (HBV) in a renal dialysis unit. Death was the result of multiple disease processes, which included active pulmonary tuberculosis and heart failure due to ischemic heart disease. There were few or no symptoms or signs of hepatitis during life other than seroconversion from negative to HBsAg positive.
Autopsy Findings[edit]
At autopsy, the liver was enlarged due primarily to severe passive congestion.
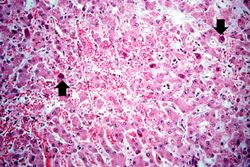
This is a low-power photomicrograph of liver from this case. This section was stained with a modified aldehyde fuchsin and counterstained with hematoxylin and eosin. Modified aldehyde fuchsin colors cystine-rich proteins--such as HBsAg and elastic fibers--deep purple. The cytoplasm of most liver cells (and RBCs) stain red due to the eosin and have dark blue nuclei.
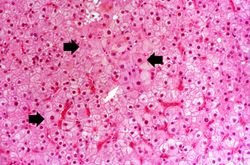
This is a higher-power photomicrograph of liver from this case. Note the severe congestion (RBCs in sinusoids) and the presence of occasional hepatocytes with dark red/magenta-stained cytoplasm (arrows).
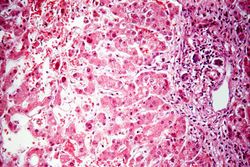
This is a higher-power photomicrograph of the periportal region exhibiting some inflammation and bile duct hyperplasia. There is also congestion and some loss of hepatocytes with disruption of the hepatic cords.
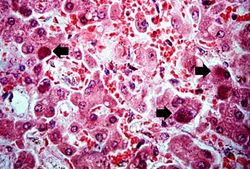
This is a high-power photomicrograph of liver with numerous hepatocytes containing accumulations of magenta-staining material in the cytoplasm (arrows).
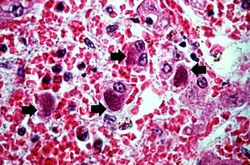
This high-power photomicrograph showing hepatocytes, the cytoplasm of which contain intracytoplasmic accumulations (arrows) of hepatitis B surface antigen.
This is a photomicrograph of a liver section from another case of hepatitis B. In this H&E-stained section, the typical "ground glass" appearance of the hepatocytes can be appreciated (arrows).
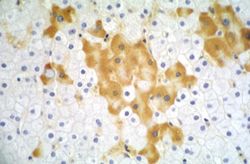
This is a low-power photomicrograph of liver from the previous image which has been reacted with antibody specific for HBsAg. The hepatocytes that contain HBsAg stain brown.
This higher-power photomicrograph of the previous section shows more clearly the HBsAg positive cells (arrows). Upon staining with H&E, these same cells exhibit a "ground glass" appearance, which is due to the accumulation of HBsAg in the hepatocyte cytoplasm.
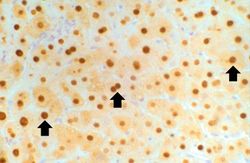
This is a low-power photomicrograph of the same liver reacted with antibody specific for hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg). The hepatocytes that contain HBcAg stain brown. Note that even at this low magnification, many brown-staining nuclei can be seen.
This high-power photomicrograph of the previous section shows the HBcAg positive nuclei (arrows).
Study Questions[edit]
HBV can produce:
- acute hepatitis,
- chronic nonprogressive hepatitis,
- progressive chronic disease ending in cirrhosis,
- fulminant hepatitis with massive liver necrosis, and
- an asymptomatic carrier state with or without progressive disease.
There is a strong association between HBV infection and the occurrence of liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma). In Taiwan, HBV infected people have a greater than 200-fold increased risk of developing liver cancer as compared with uninfected individuals. However, the precise role of HBV in the causation of human liver cancer is not clear.
With hepatotropic viruses, there are those who:
- harbor one of the viruses but suffer little or no adverse effects (a "healthy" carrier) and those who
- have chronic disease but are essentially free of symptoms or disability.
Both constitute reservoirs of infection. HBV infection early in life, particularly via vertical transmission during childbirth, produces a carrier state 90 to 95% of the time. In contrast, only 1 to 10% of adult infections yield a carrier state. Individuals with impaired immunity are more likely to become carriers.
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
Journal Articles[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]