Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 8:HSV Glossitis"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
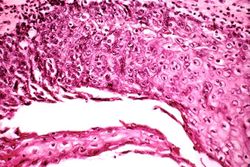
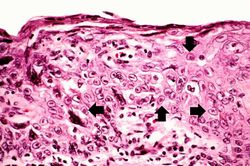
File:IPLab8HSVGlossitis5.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of epithelium near the edge of the ulcer. The cells that have been invaded by the herpes virus contain intranuclear accumulations of amphophilic viral inclusions (arrows). | File:IPLab8HSVGlossitis5.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of epithelium near the edge of the ulcer. The cells that have been invaded by the herpes virus contain intranuclear accumulations of amphophilic viral inclusions (arrows). | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Study Questions == | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What are the various types of herpes viruses?">Eight types of herpes viruses, belonging to three groups, have been isolated from humans: | ||
| + | * neurotropic alpha-group viruses, including HSV-1, HSV-2, and varicella-zoster (VZV); | ||
| + | * lymphotropic beta-group viruses, including CMV, human herpes virus 6 (which causes exanthem subitum, a benign rash of infants), and human herpes virus 7 (which is not yet associated with a specific disease); and | ||
| + | * gamma-group virus, EBV.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is the most likely herpes virus that would cause this ulcerative glossitis?">This ulcerative glossitis is likely caused by herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1).</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What makes up the intranuclear inclusion bodies seen in herpes virus infections?">All HSV lesions are marked by formation of large pink-to-purple (Cowdry type A) intranuclear inclusions that contain intact and disrupted virions. These inclusions push the host cell chromatin to the edges of the nucleus. Although cell and nuclear size increase only slightly, herpes virus produces inclusion-bearing multinucleated syncytia, which are diagnostic in smears of blister fluid (Tzanck test).</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="How does HSV-1 kill a cell?">Herpes viral proteins insert into the host cell’s plasma membrane and directly damage the membrane's integrity.</spoiler> | ||
| + | * <spoiler text="What is latency?">During a primary herpetic infection, the herpes virus invades nerve endings in the mucosa, travels up the axons of these nerves, and infects regional ganglia. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Following the primary infection, the patient becomes asymptomatic for a period--being infected by the virus but not showing clinical manifestations is known as latency. | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, occasionally the latent virus residing in a ganglion can become reactivated, descend the axon, and reinfect the area served by that particular ganglion.</spoiler> | ||
{{IPLab 8}} | {{IPLab 8}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 8]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 8]] | ||
Revision as of 15:44, 21 August 2013
Clinical Summary[edit]
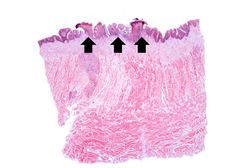
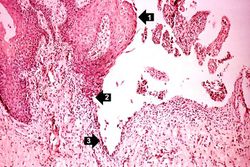
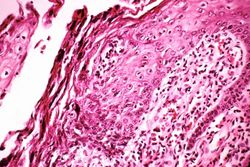
During the course of a postmortem examination of a 58-year-old female, the tongue was noted to have a number of multiple shallow ulcers. This was an incidental finding and not related to the patient's primary disease process.
Images[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
| |||||
An infiltrate is an accumulation of cells in the lung parenchyma--this is a sign of pneumonia.