Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 8:HSV Encephalitis"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Clinical Summary == | == Clinical Summary == | ||
| − | This 30-year-old white male experienced a generalized tonic-clonic seizure and was subsequently started on a course of Dilantin. He did well, but later developed a headache lasting over a week, which was associated with tonic-clonic seizures, fever, and--toward the end of this period--ataxia. The patient improved and returned to work, but the headache returned. A lumbar puncture was then performed which showed 22 cells/ | + | This 30-year-old white male experienced a generalized tonic-clonic seizure and was subsequently started on a course of Dilantin. He did well, but later developed a headache lasting over a week, which was associated with tonic-clonic seizures, fever, and--toward the end of this period--ataxia. The patient improved and returned to work, but the headache returned. A lumbar puncture was then performed which showed 22 cells/mm³ (all lymphocytes), protein of 88 grams/L, and a glucose level of 49 mg/dL (with a simultaneous serum glucose of 83 mg/dL). These findings were compatible with a viral infection. Despite therapy, the patient had another seizure and again developed fever. At that time, a brain biopsy was performed which showed herpetic encephalitis. Despite aggressive antiviral therapy the patient died. |
== Images == | == Images == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
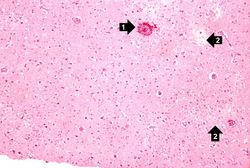
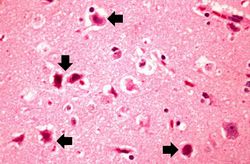
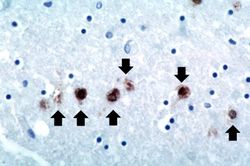
IPLab8HSVEncephalitis12.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of a brain section stained with an antibody against herpes simplex. Even at this magnification, it is easy to pick out cells that are positive for the virus (arrows). | IPLab8HSVEncephalitis12.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of a brain section stained with an antibody against herpes simplex. Even at this magnification, it is easy to pick out cells that are positive for the virus (arrows). | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Virtual Microscopy == | ||
| + | <peir-vm>IPLab8HSVEncephalitis</peir-vm> | ||
== Study Questions == | == Study Questions == | ||
| Line 25: | Line 28: | ||
== Additional Resources == | == Additional Resources == | ||
=== Reference === | === Reference === | ||
| − | + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/218580-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Herpes Simplex] | |
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/783113-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Herpes Simplex in Emergency Medicine] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1165183-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Herpes Simplex Encephalitis] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/infectious_diseases/herpesviruses/herpes_simplex_virus_hsv_infections.html Merck Manual: Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Infections] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/neurologic_disorders/brain_infections/encephalitis.html Merck Manual: Encephalitis] | ||
=== Journal Articles === | === Journal Articles === | ||
| − | + | * Edlow JA, Panagos PD, Godwin SA, Thomas TL, Decker WW; American College of Emergency Physicians. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18809105 Clinical policy: critical issues in the evaluation and management of adult patients presenting to the emergency department with acute headache]. ''Ann Emerg Med'' 2008 Oct;52(4):407-36. | |
| + | * Thomson RB Jr, Bertram H. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11780267 Laboratory diagnosis of central nervous system infections]. ''Infect Dis Clin North Am'' 2001 Dec;15(4):1047-71. | ||
=== Images === | === Images === | ||
| − | + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/127-herpes PEIR Digital Library: Herpes Images] | |
| + | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/CNSHTML/CNSIDX.html#6 WebPath: CNS Infections] | ||
== Related IPLab Cases == | == Related IPLab Cases == | ||
| − | + | * [[IPLab:Lab 8:HSV Glossitis|Lab 8: Herpes Glossitis]] | |
{{IPLab 8}} | {{IPLab 8}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 8]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 8]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:28, 3 January 2014
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
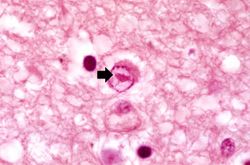
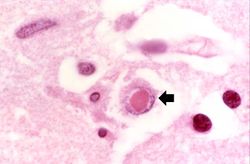
This 30-year-old white male experienced a generalized tonic-clonic seizure and was subsequently started on a course of Dilantin. He did well, but later developed a headache lasting over a week, which was associated with tonic-clonic seizures, fever, and--toward the end of this period--ataxia. The patient improved and returned to work, but the headache returned. A lumbar puncture was then performed which showed 22 cells/mm³ (all lymphocytes), protein of 88 grams/L, and a glucose level of 49 mg/dL (with a simultaneous serum glucose of 83 mg/dL). These findings were compatible with a viral infection. Despite therapy, the patient had another seizure and again developed fever. At that time, a brain biopsy was performed which showed herpetic encephalitis. Despite aggressive antiviral therapy the patient died.
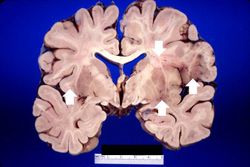
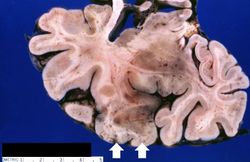
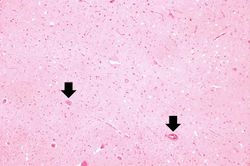
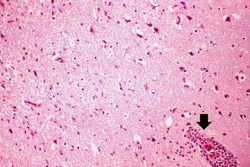
Images[edit]
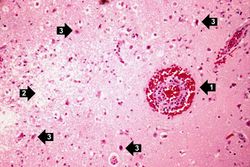
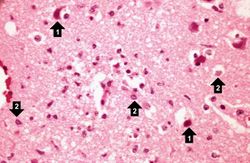
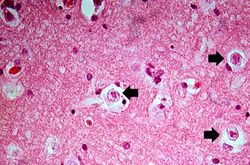
This is a high-power photomicrograph of the previous section. At this power it is easier to see the blood vessel with the perivascular hemorrhage and mild perivascular lymphocytic cuffing (1). In addition, the areas of edema and loss of neurophil (2) can be better appreciated. Red shrunken neurons and glia with pyknotic nuclei (3) are also evident at this power.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Herpes Simplex
- eMedicine Medical Library: Herpes Simplex in Emergency Medicine
- eMedicine Medical Library: Herpes Simplex Encephalitis
- Merck Manual: Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Infections
- Merck Manual: Encephalitis
Journal Articles[edit]
- Edlow JA, Panagos PD, Godwin SA, Thomas TL, Decker WW; American College of Emergency Physicians. Clinical policy: critical issues in the evaluation and management of adult patients presenting to the emergency department with acute headache. Ann Emerg Med 2008 Oct;52(4):407-36.
- Thomson RB Jr, Bertram H. Laboratory diagnosis of central nervous system infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2001 Dec;15(4):1047-71.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
| |||||
A tonic-clonic seizure involves loss of consciousness followed by tonic, then clonic, convulsions.
A tonic-clonic seizure involves loss of consciousness followed by tonic, then clonic, convulsions.
A normal number of cells in CSF is <4 lymphocytes per mm³.
A normal protein level for CSF should be < 0.4 grams/L.
A normal CSF glucose level should be approximately 70% of the patient's serum glucose level.
An infiltrate is an accumulation of cells in the lung parenchyma--this is a sign of pneumonia.