Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 3:Bronchopneumonia"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) (Created page with "<gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> File:IPLab3Bronchopneumonia1.jpg|This gross photograph of lung illustrates multiple abscesses throughout the lung of this patient. Fil...") |
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Images == | ||
<gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> | <gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> | ||
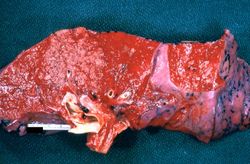
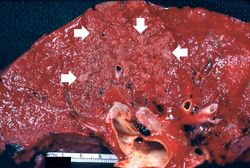
File:IPLab3Bronchopneumonia1.jpg|This gross photograph of lung illustrates multiple abscesses throughout the lung of this patient. | File:IPLab3Bronchopneumonia1.jpg|This gross photograph of lung illustrates multiple abscesses throughout the lung of this patient. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
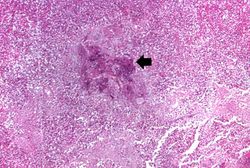
File:IPLab3Bronchopneumonia7.jpg|This higher-power photomicrograph shows a central portion of an abscess. Note the absence of any parenchymal lung tissue in this section due to extensive neutrophilic infiltration with liquefaction necrosis of the parenchymal tissue. Masses of leukocytes (primarily neutrophils), fluid ("liquor puris" which is serum, fibrin, etc.), and necrotic debris within an abscess form what is referred to as "purulent material" -- or "pus" in lay terminology. The blue-staining mass in the center of this abscess (arrow) represents colonies of bacteria. | File:IPLab3Bronchopneumonia7.jpg|This higher-power photomicrograph shows a central portion of an abscess. Note the absence of any parenchymal lung tissue in this section due to extensive neutrophilic infiltration with liquefaction necrosis of the parenchymal tissue. Masses of leukocytes (primarily neutrophils), fluid ("liquor puris" which is serum, fibrin, etc.), and necrotic debris within an abscess form what is referred to as "purulent material" -- or "pus" in lay terminology. The blue-staining mass in the center of this abscess (arrow) represents colonies of bacteria. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{IPLab 3}} | ||
Revision as of 03:24, 19 August 2013
Images[edit]
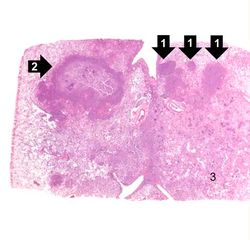
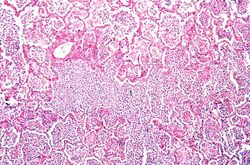
This is a low-power photomicrograph of lung with multiple focal lesions (1) throughout the tissue, some of which have a pale center indicating a loss of parenchymal tissue (2). This is typical of abscess formation in the lung and represents a form of liquefaction necrosis. This pneumonia is bronchopneumonia since the distribution is along the bronchi and the terminal airway distribution throughout the lung. Note that there are some areas of lung which appear relatively normal, having a pale-staining appearance. Other areas, such as in the lower central area (3), are much darker, indicating a heavy cellular infiltrate.
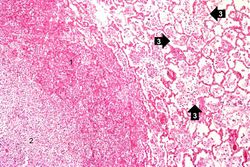
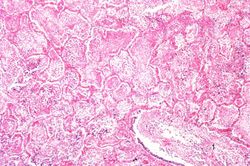
This photomicrograph of the wall of an abscess (1) illustrates liquefaction necrosis in the center of the abscess (2). The remaining lung parenchyma (on the right side of the image) has extensive neutrophilic infiltration into the alveoli (3). This abscess has destroyed a portion of the lung, but other areas of the lung where the normal structure has been retained could recover normal function.
This higher-power photomicrograph shows a central portion of an abscess. Note the absence of any parenchymal lung tissue in this section due to extensive neutrophilic infiltration with liquefaction necrosis of the parenchymal tissue. Masses of leukocytes (primarily neutrophils), fluid ("liquor puris" which is serum, fibrin, etc.), and necrotic debris within an abscess form what is referred to as "purulent material" -- or "pus" in lay terminology. The blue-staining mass in the center of this abscess (arrow) represents colonies of bacteria.
An abscess is a collection of pus (white blood cells) within a cavity formed by disintegrated tissue.
An abscess is a collection of pus (white blood cells) within a cavity formed by disintegrated tissue.
In alcoholics, aspiration pneumonia is common--bacteria enter the lung via aspiration of gastric contents.
An infiltrate is an accumulation of cells in the lung parenchyma--this is a sign of pneumonia.