File:IPLab3Bronchopneumonia4.jpg
Revision as of 03:23, 19 August 2013 by Seung Park (talk | contribs) (This photomicrograph of the wall of an abscess (1) illustrates liquefaction necrosis in the center of the abscess (2). The remaining lung parenchyma (on the right side of the image) has extensive neutrophilic infiltration into the alveoli (3). This abs...)
IPLab3Bronchopneumonia4.jpg (675 × 450 pixels, file size: 94 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
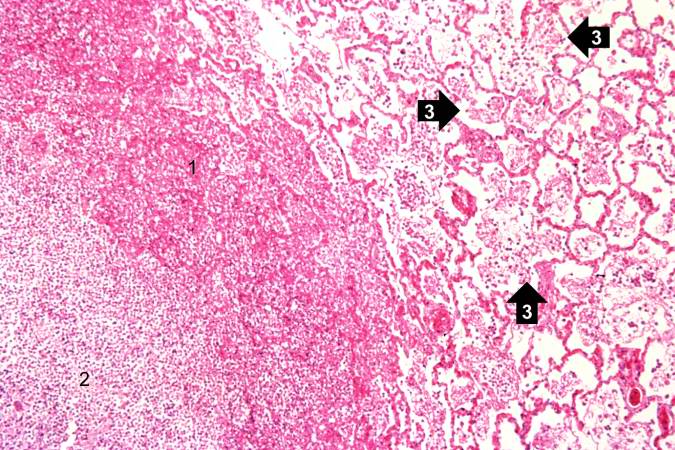
This photomicrograph of the wall of an abscess (1) illustrates liquefaction necrosis in the center of the abscess (2). The remaining lung parenchyma (on the right side of the image) has extensive neutrophilic infiltration into the alveoli (3). This abscess has destroyed a portion of the lung, but other areas of the lung where the normal structure has been retained could recover normal function.
An abscess is a collection of pus (white blood cells) within a cavity formed by disintegrated tissue.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 03:23, 19 August 2013 |  | 675 × 450 (94 KB) | Seung Park (talk | contribs) | This photomicrograph of the wall of an abscess (1) illustrates liquefaction necrosis in the center of the abscess (2). The remaining lung parenchyma (on the right side of the image) has extensive neutrophilic infiltration into the alveoli (3). This abs... |
- You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page links to this file: