From Pathology Education Instructional Resource
|
|
| Line 9: |
Line 9: |
| | | | |
| | ===Resident Questions=== | | ===Resident Questions=== |
| − | * <spoiler text="Diagnosis?"> | + | * <spoiler text="Diagnosis?">__NOGLOSSARY__ |
| | * Pseudocyst | | * Pseudocyst |
| | ** Most common cystic lesion | | ** Most common cystic lesion |
| Line 23: |
Line 23: |
| | ** Lack a true epithelial lining | | ** Lack a true epithelial lining |
| | </spoiler> | | </spoiler> |
| − | * <spoiler text="What are some of the cytologic features that lead you to the diagnosis?"> | + | * <spoiler text="What are some of the cytologic features that lead you to the diagnosis?">__NOGLOSSARY__ |
| | * Variable acute and chronic inflammation | | * Variable acute and chronic inflammation |
| | * Histiocytes | | * Histiocytes |
Revision as of 20:08, 16 January 2014
Cytology
Resident Questions
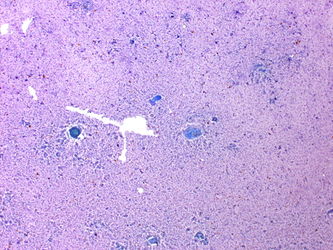
- Pseudocyst
- Most common cystic lesion
- Etiology is diverse (acute pancreatitis, recurrent chronic pancreatitis, trauma, chronic alcohol abuse)
- Clinically patients present with jaundice, pain, nausea, vomiting, weight loss
- Pathogenesis
- leakage of pancreatic enzymes into parenchyma
- necrosis and chemical peritonitis
- inflammatory response and pancreatic secretion accumulation occurs and fibrous tissue walls off irritants which causes cyst formation
- Localized collection of amylase rich pancreatic secretions, necrotic debris and blood
- Most occur in the tail of the pancreas
- Usually solitary and unilocular
- Lack a true epithelial lining
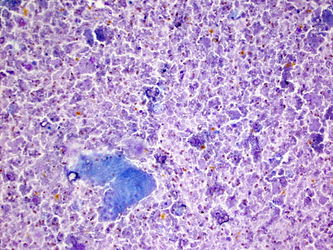
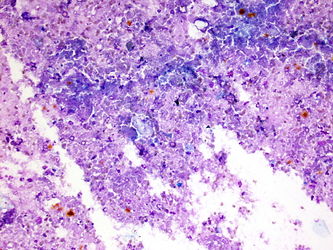
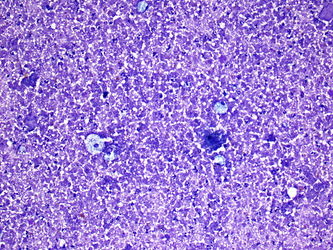
- Variable acute and chronic inflammation
- Histiocytes
- Giant cells
- Necrotic debris
- Granulation tissue may be present
- No epithelium with atypia
- Ductal adenocarcinoma with cystic degeneration
- Atypia in the epithelium
- Pleomorphic nuclei, cytoplasm variable (vacuolated to dense)
- Cellular inflammatory background
- Positive CEA and cytokeratin
- Any neoplasm will have epithelial groups and single cells with atypia
- Big diagnostic problem is the atypia that can be seen in the granulation tissue