Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 3:Sarcoidosis"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
(→Journal Articles) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> | <gallery heights="250px" widths="250px"> | ||
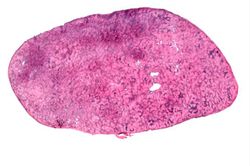
File:IPLab3Sarcoidosis1.jpg|This is a low-power photomicrograph of a lymph node. Note the rather pale-pink color of the tissue with dark-staining cells found in only a few scattered areas. These darker cells represent the original lymphocytes of this lymphoid organ. | File:IPLab3Sarcoidosis1.jpg|This is a low-power photomicrograph of a lymph node. Note the rather pale-pink color of the tissue with dark-staining cells found in only a few scattered areas. These darker cells represent the original lymphocytes of this lymphoid organ. | ||
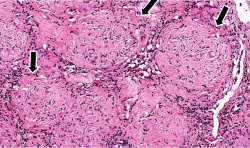
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab3Sarcoidosis2b.jpg|This photomicrograph of lymph node tissue illustrates a paucity of lymphocytes as well as numerous small, pale-staining nodules (arrows) throughout the tissue. |
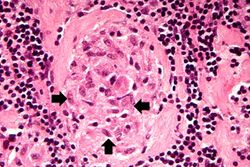
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab3Sarcoidosis3b.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of the small nodules (arrows) seen in the previous image. Close examination reveals that they are composed of large macrophages (epithelioid macrophages). These small granulomas form multiple series of reaction centers throughout the lymph node. Note the remaining lymphocytes surrounding the granulomas. |
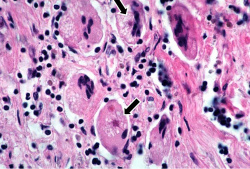
File:IPLab3Sarcoidosis4.jpg|This photomicrograph of a single granuloma illustrates the individual macrophages (arrows) which make up the bulk of this tissue. There is an absence of necrosis in the center of the lesions in this case. | File:IPLab3Sarcoidosis4.jpg|This photomicrograph of a single granuloma illustrates the individual macrophages (arrows) which make up the bulk of this tissue. There is an absence of necrosis in the center of the lesions in this case. | ||
| − | File: | + | File:IPLab3Sarcoidosis5b.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of a multinucleated giant cell (1). In the center of this foreign body-containing giant cell there is a small asteroid body (2). There is no functional significance to this asteroid body. |
| − | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | + | == Virtual Microscopy == | |
| + | === Lymph Node: Sarcoidosis === | ||
| + | <peir-vm>IPLab3Sarcoidosis</peir-vm> | ||
| + | === Lymph Node === | ||
| + | <peir-vm>UAB-Histology-00035</peir-vm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Study Questions == | ||
* <spoiler text="What is sarcoidosis?">The exact cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Sarcoidosis is characterized by non-caseating granulomas in many tissues and organs.</spoiler> | * <spoiler text="What is sarcoidosis?">The exact cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Sarcoidosis is characterized by non-caseating granulomas in many tissues and organs.</spoiler> | ||
* <spoiler text="What is the characteristic phenotype of sarcoid granulomas?">The typical characteristic of a sarcoid granuloma is a non-caseating granuloma which consists of an aggregate of tightly-clustered epitheliod cells, often with Langhans’ or multinucleated giant cells. Occasionally, asteroid bodies may be seen.</spoiler> | * <spoiler text="What is the characteristic phenotype of sarcoid granulomas?">The typical characteristic of a sarcoid granuloma is a non-caseating granuloma which consists of an aggregate of tightly-clustered epitheliod cells, often with Langhans’ or multinucleated giant cells. Occasionally, asteroid bodies may be seen.</spoiler> | ||
* <spoiler text="What are asteroid bodies and are they pathognomonic for sarcoid or are they seen in other diseases?">Asteroid bodies are stellate inclusions within giant cells. They are not pathognomonic for sarcoid; they can be seen in other granulomatous disease processes (e.g., berylliosis).</spoiler> | * <spoiler text="What are asteroid bodies and are they pathognomonic for sarcoid or are they seen in other diseases?">Asteroid bodies are stellate inclusions within giant cells. They are not pathognomonic for sarcoid; they can be seen in other granulomatous disease processes (e.g., berylliosis).</spoiler> | ||
| − | {{ | + | == Additional Resources == |
| + | === Reference === | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/809047-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Acute Complications of Sarcoidosis] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/301914-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Sarcoidosis] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123970-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Dermatologic Manifestations of Sarcoidosis] | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1147324-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Neurosarcoidosis] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/pulmonary_disorders/sarcoidosis/sarcoidosis.html Merck Manual: Sarcoidosis] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Journal Articles === | ||
| + | * Drent M, Crouser ED, Grunewald J. [https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra2101555 Challenges of Sarcoidosis and Its Management]. ''N Engl J Med'' 2021; 385:1018-1032 | ||
| + | * English JC, Patel PJ, Greer KE. [http://www.mdconsult.com/das/article/body/421068364-2/jorg=journal&source=MI&sp=11817316&sid=119276088/N/217466/1.html?issn= Sarcoidosis]. ''J Am Acad Dermatol'' 2001;44:725-43 | ||
| + | * Johns CJ, Michele TM. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10195091 The clinical management of sarcoidosis. A 50-year experience at the Johns Hopkins Hospital]. ''Medicine (Baltimore)'' 1999 Mar;78(2):65-111. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Images === | ||
| + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/531-sarcoidosis PEIR Digital Library: Sarcoidosis Images] | ||
| + | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/LUNGHTML/LUNGIDX.html#2 WebPath: Granulomatous Disease] | ||
| + | == Related IPLab Cases == | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 2:Metastatic Calcification|Lab 2: Lung: Metastatic Calcification]] | ||
| + | {{IPLab 3}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 3]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 3]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:16, 13 September 2021
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
This 33-year-old white female was admitted for evaluation of abnormal findings on a chest x-ray. She was asymptomatic and a physical examination revealed no significant abnormalities. Laboratory results indicated hypercalcemia and elevated gamma globulin. Radiographic examination showed enlarged subcarinal, hilar, and right paratracheal lymph nodes. A right paratracheal lymph node was biopsied. Special stains for acid-fast bacilli and fungi were negative and a diagnosis of sarcoidosis was made.
Images[edit]
This is a photomicrograph of the small nodules (arrows) seen in the previous image. Close examination reveals that they are composed of large macrophages (epithelioid macrophages). These small granulomas form multiple series of reaction centers throughout the lymph node. Note the remaining lymphocytes surrounding the granulomas.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Lymph Node: Sarcoidosis[edit]
Lymph Node[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Acute Complications of Sarcoidosis
- eMedicine Medical Library: Sarcoidosis
- eMedicine Medical Library: Dermatologic Manifestations of Sarcoidosis
- eMedicine Medical Library: Neurosarcoidosis
- Merck Manual: Sarcoidosis
Journal Articles[edit]
- Drent M, Crouser ED, Grunewald J. Challenges of Sarcoidosis and Its Management. N Engl J Med 2021; 385:1018-1032
- English JC, Patel PJ, Greer KE. Sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001;44:725-43
- Johns CJ, Michele TM. The clinical management of sarcoidosis. A 50-year experience at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. Medicine (Baltimore) 1999 Mar;78(2):65-111.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
Hypercalcemia is the state of having increased levels of calcium in the blood.