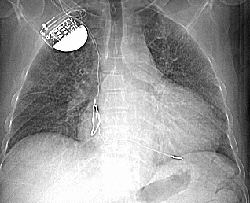
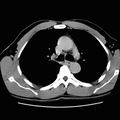
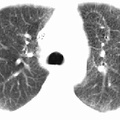
RADIOLOGY: CHEST: Case# 9: AMIODARONE TOXICITY. 52 year old male with a history of ventricular tachyarrythmias. There is diffuse, increased bilateral interstitial pulmonary markings in a reticular nodular pattern, most prominent in the lung bases and posteriorly. No evidence of focal pulmonary infiltrates or masses identified. The pleura appears unremarkable. No pneumothorax or pleural effusion. There is mild cardiomegaly with right atrial and right ventricular wires in place. There is diffuse homogeneously increased hepatoparenchymal radiodensity without evidence of focal lesions or intrahepatic biliary duct dilatation noted. Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic drug used for supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias. It has significant side effects, the most notable being pulmonary fibrosis. This is best visualized on HRCT. Pulmonary fibrosis causes a cystic appearance, or honeycombing, within the lungs. There is often associated septal and pleural thickening and high density pleuroparenchymal plaques near the lung bases. In addition, there may be increased liver density without a marked change in splenic attenuation due to accumulation of the drug, which contains iodine, within the hepatocytes.
- Author
- Peter Anderson
- Posted on
- Thursday 1 August 2013
- Tags
- Chest, cystic fibrosis, radiology
- Albums
- Visits
- 4071
0 comments