Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 7:Esophagus SCC"
Seung Park (talk | contribs) |
(→Clinical Summary) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Approximately six months prior to admission, this 78-year-old male began having difficulty in swallowing solid food. This difficulty was described as a sticking of the food in his throat and was accompanied by cramping pain which could only be relieved by "coughing up" the ingested food. This dysphagia was accompanied by a twenty-pound weight loss. Following an upper GI series and endoscopic biopsy, the patient was given radiation treatment with considerable improvement. He did well for four months, after which the dysphagia and weight loss increased markedly. He refused operative intervention or further treatment and he died at home two months later. | Approximately six months prior to admission, this 78-year-old male began having difficulty in swallowing solid food. This difficulty was described as a sticking of the food in his throat and was accompanied by cramping pain which could only be relieved by "coughing up" the ingested food. This dysphagia was accompanied by a twenty-pound weight loss. Following an upper GI series and endoscopic biopsy, the patient was given radiation treatment with considerable improvement. He did well for four months, after which the dysphagia and weight loss increased markedly. He refused operative intervention or further treatment and he died at home two months later. | ||
| − | + | An autopsy revealed a circumferential fungating mass in the distal third of the esophagus. This mass partially occluded the lumen of the esophagus. | |
| − | An autopsy revealed a circumferential fungating mass in the distal third of the esophagus. This mass partially occluded the lumen of the esophagus. | ||
== Images == | == Images == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
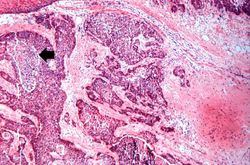
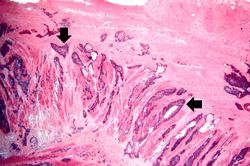
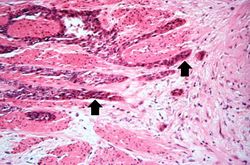
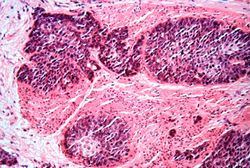
File:IPLab7EsophSCC7.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of the tumor cells that have invaded the adjacent muscle tissue. | File:IPLab7EsophSCC7.jpg|This is a high-power photomicrograph of the tumor cells that have invaded the adjacent muscle tissue. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Virtual Microscopy == | ||
| + | <peir-vm>IPLab7EsophSCC</peir-vm> | ||
== Study Questions == | == Study Questions == | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
* genetic (racial) predisposition.</spoiler> | * genetic (racial) predisposition.</spoiler> | ||
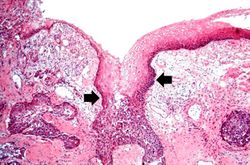
* <spoiler text="What factors facilitate growth and spread of this tumor?">The rich lymphatic network in the submucosa of the esophagus promotes extensive circumferential and longitudinal spread. Intramural tumor cell clusters are often seen several centimeters away from the main tumor mass. Local extension into adjacent mediastinal structures occurs early and often in this disease and seriously limits the chance of curative resection.</spoiler> | * <spoiler text="What factors facilitate growth and spread of this tumor?">The rich lymphatic network in the submucosa of the esophagus promotes extensive circumferential and longitudinal spread. Intramural tumor cell clusters are often seen several centimeters away from the main tumor mass. Local extension into adjacent mediastinal structures occurs early and often in this disease and seriously limits the chance of curative resection.</spoiler> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Additional Resources == | ||
| + | === Reference === | ||
| + | * [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1965430-overview eMedicine Medical Library: Head and Neck Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/dermatologic_disorders/cancers_of_the_skin/overview_of_skin_cancer.html Merck Manual: Overview of Skin Cancer] | ||
| + | * [http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/dermatologic_disorders/cancers_of_the_skin/squamous_cell_carcinoma.html Merck Manual: Squamous Cell Carcinoma] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Journal Articles === | ||
| + | * Shibata H, Matsubara O. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11472561 Apoptosis as an independent prognostic indicator in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus]. ''Pathol Int'' 2001 Jul;51(7):498-503. | ||
| + | * Wu S, Powers S, Zhu W, Hannun YA. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4836858/ Substantial contribution of extrinsic risk factors to cancer development]. ''Nature'' 2016 Jan 7; 529(7584): 43–47. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Images === | ||
| + | * [{{SERVER}}/library/index.php?/tags/254-squamous_cell_carcinoma PEIR Digital Library: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Images] | ||
| + | * [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/NEOHTML/NEOPLIDX.html WebPath: Neoplasia] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Related IPLab Cases == | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 7:Lip SCC|Lab 7: Lip: Squamous Cell Carcinoma]] | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 7:IDC|Lab 7: Breast: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma]] | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 7:Bronchogenic Carcinoma|Lab 7: Lung: Bronchogenic Carcinoma]] | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 7:Adenocarcinoma|Lab 7: Colon: Adenocarcinoma]] | ||
| + | * [[IPLab:Lab 7:Metastatic Adenocarcinoma|Lab 7: Lung & Liver: Metastatic Adenocarcinoma]] | ||
{{IPLab 7}} | {{IPLab 7}} | ||
[[Category: IPLab:Lab 7]] | [[Category: IPLab:Lab 7]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:11, 9 July 2020
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
Approximately six months prior to admission, this 78-year-old male began having difficulty in swallowing solid food. This difficulty was described as a sticking of the food in his throat and was accompanied by cramping pain which could only be relieved by "coughing up" the ingested food. This dysphagia was accompanied by a twenty-pound weight loss. Following an upper GI series and endoscopic biopsy, the patient was given radiation treatment with considerable improvement. He did well for four months, after which the dysphagia and weight loss increased markedly. He refused operative intervention or further treatment and he died at home two months later.
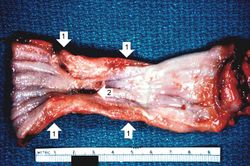
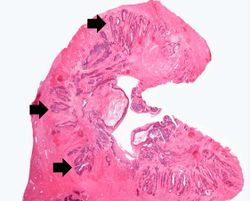
An autopsy revealed a circumferential fungating mass in the distal third of the esophagus. This mass partially occluded the lumen of the esophagus.
Images[edit]
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Head and Neck Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Merck Manual: Overview of Skin Cancer
- Merck Manual: Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Journal Articles[edit]
- Shibata H, Matsubara O. Apoptosis as an independent prognostic indicator in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Pathol Int 2001 Jul;51(7):498-503.
- Wu S, Powers S, Zhu W, Hannun YA. Substantial contribution of extrinsic risk factors to cancer development. Nature 2016 Jan 7; 529(7584): 43–47.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
- Lab 7: Lip: Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Lab 7: Breast: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma
- Lab 7: Lung: Bronchogenic Carcinoma
- Lab 7: Colon: Adenocarcinoma
- Lab 7: Lung & Liver: Metastatic Adenocarcinoma
An upper GI series is a series of barium-aided radiographs involving the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.