IPLab:Lab 3:Bronchopneumonia
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
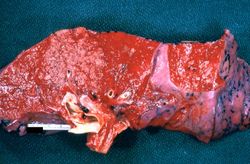
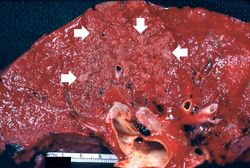
This 15-year-old black female sustained third degree burns involving approximately 85% of the body surface. On admission to the hospital, the patient was taken to the operating room where a tracheotomy was performed and her burned body surface was debrided. After a few days of hospitalization, the peripheral white blood count was 41,000 cells/mm³ with a shift to the left. In spite of intensive therapy, which included administration of fluids and antibiotics, the patient expired on the sixth hospital day.
Autopsy Findings[edit]
Each lung weighed approximately 630 grams and was studded with gray nodules which ranged in size from 3 to 6 mm in diameter. In several areas, these coalesced to form nodules having necrotic-appearing centers.
Images[edit]
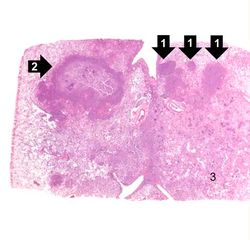
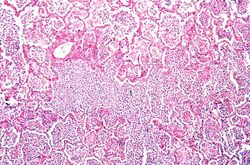
This is a low-power photomicrograph of lung with multiple focal lesions (1) throughout the tissue, some of which have a pale center indicating a loss of parenchymal tissue (2). This is typical of abscess formation in the lung and represents a form of liquefaction necrosis. This pneumonia is bronchopneumonia since the distribution is along the bronchi and the terminal airway distribution throughout the lung. Note that there are some areas of lung which appear relatively normal, having a pale-staining appearance. Other areas, such as in the lower central area (3), are much darker, indicating a heavy cellular infiltrate.
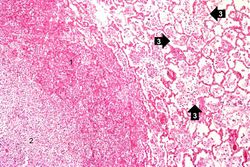
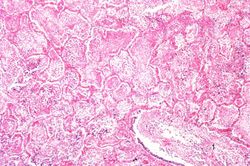
This photomicrograph of the wall of an abscess (1) illustrates liquefaction necrosis in the center of the abscess (2). The remaining lung parenchyma (on the right side of the image) has extensive neutrophilic infiltration into the alveoli (3). This abscess has destroyed a portion of the lung, but other areas of the lung where the normal structure has been retained could recover normal function.
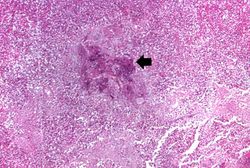
This higher-power photomicrograph shows a central portion of an abscess. Note the absence of any parenchymal lung tissue in this section due to extensive neutrophilic infiltration with liquefaction necrosis of the parenchymal tissue. Masses of leukocytes (primarily neutrophils), fluid ("liquor puris" which is serum, fibrin, etc.), and necrotic debris within an abscess form what is referred to as "purulent material" -- or "pus" in lay terminology. The blue-staining mass in the center of this abscess (arrow) represents colonies of bacteria.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
Lung: Bronchopneumonia[edit]
Normal Lung[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Empyema and Abscess Pneumonia
- eMedicine Medical Library: Aspiration Pneumonia
- eMedicine Medical Library: Bacterial Pneumonia
- Merck Manual: Overview of Pneumonia
Journal Articles[edit]
- Katz DS, Leung AN. Radiology of pneumonia. Clin Chest Med 1999 Sep;20(3):549-62.
Images[edit]
Related IPLab Cases[edit]
A normal white blood cell count is 4,000 to 11,000 cells per cubic mm.
A shift to the left indicates an increased ratio of immature PMNs (bands) to mature PMNs (segs).
A normal adult left lung weighs 375 grams (range: 325 to 480 grams). And a normal adult right lung weighs 450 grams (range: 360 to 570 grams).
An abscess is a collection of pus (white blood cells) within a cavity formed by disintegrated tissue.
An abscess is a collection of pus (white blood cells) within a cavity formed by disintegrated tissue.
In alcoholics, aspiration pneumonia is common--bacteria enter the lung via aspiration of gastric contents.
An infiltrate is an accumulation of cells in the lung parenchyma--this is a sign of pneumonia.