IPLab:Lab 11:Cysticercosis
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
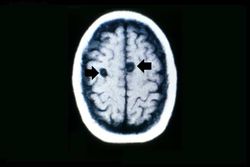
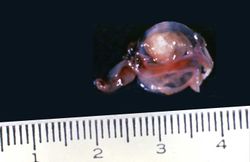
This 29-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital because of repeated tonic-clonic seizures. The patient was a tour guide leading groups of tourist to Tibet for two-month walking/camping tours in the Himalayas. Her seizures were easily controlled by intravenous administration of phenytoin. The WBC count was 13,000, with 5% eosinophils and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate was slightly elevated. A cranial CT performed with and without contrast revealed two ring-enhancing lesions. The patient underwent a craniotomy and excisional biopsy.
Images[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Cysticercosis
- eMedicine Medical Library: Cysticercosis in Emergency Medicine
- Merck Manual: Taeniasis Solium and Cysticercosis
Journal Articles[edit]
- Garcia HH, Del Brutto OH. Taenia solium cysticercosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2000 Mar;14(1):97-119, ix.
Images[edit]
| |||||
A tonic-clonic seizure involves loss of consciousness followed by tonic, then clonic, convulsions.
A normal white blood cell count is 4000-11,000 cells/mm³.
An elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a non-specific indicator of inflammation.