Difference between revisions of "IPLab:Lab 10:Blastomycosis"
(→Autopsy Findings) |
(→Clinical Summary) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Clinical Summary == | == Clinical Summary == | ||
| + | About three weeks before his death, this 17-year-old white male developed a "chest cold" which gradually worsened. The patient was eventually admitted three days before his death. At that time, the patient was very dyspneic. Chest x-ray showed consolidation of the entire left lung. The initial impression by his care team was staphylococcal pneumonia. However, Blastomyces dermatitides was identified in stained smears of sputum the next day. In spite of appropriate antifungal therapy, the patient deteriorated rapidly and died. | ||
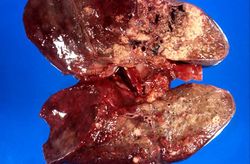
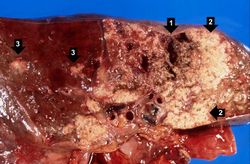
| − | + | At autopsy the entire left lung was consolidated and had multiple hemorrhagic areas. | |
== Images == | == Images == | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 9 July 2020
Contents
Clinical Summary[edit]
About three weeks before his death, this 17-year-old white male developed a "chest cold" which gradually worsened. The patient was eventually admitted three days before his death. At that time, the patient was very dyspneic. Chest x-ray showed consolidation of the entire left lung. The initial impression by his care team was staphylococcal pneumonia. However, Blastomyces dermatitides was identified in stained smears of sputum the next day. In spite of appropriate antifungal therapy, the patient deteriorated rapidly and died.
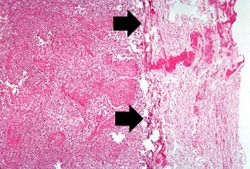
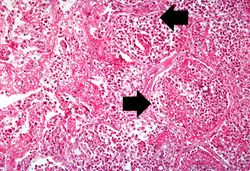
At autopsy the entire left lung was consolidated and had multiple hemorrhagic areas.
Images[edit]
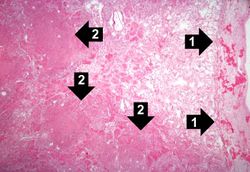
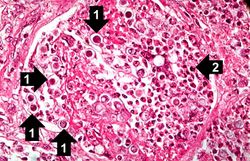
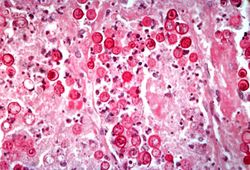
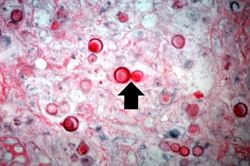
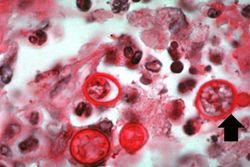
This high-power photomicrograph shows an alveolus filled with numerous round bodies up to 25 mm in diameter. Some of these double-contour bodies (1) have a dense center and a clear halo. These are the Blastomyces organisms. The typical B. dermatitides organism is smoothly-outlined with a central, densely basophilic cytoplasm surrounded by a clear halo. When stained with hematoxylin and eosin, the organism is outlined by a relatively thick cell wall. There are also numerous inflammatory cells (2) in the alveolus--neutrophils, lymphocytes and macrophages--which produce a pyogranulomatous inflammatory reaction.
Virtual Microscopy[edit]
H&E[edit]
PAS[edit]
Study Questions[edit]
Additional Resources[edit]
Reference[edit]
- eMedicine Medical Library: Imaging in Thoracic Blastomycosis
- eMedicine Medical Library: Blastomycosis
- Merck Manual: Blastomycosis
Journal Articles[edit]
- Rooney PJ, Klein BS. Linking fungal morphogenesis with virulence. Cell Microbiol 2002 Mar;4(3):127-37.
Images[edit]
| |||||
In alcoholics, aspiration pneumonia is common--bacteria enter the lung via aspiration of gastric contents.
Consolidation is the filling of lung air spaces with exudate--this is a sign of pneumonia.